- GOLD IRA
- Download Our 2024 Precious Metals IRA Investor’s Guide.
Click Here  Gold IRA
Gold IRA
 Investing
Investing
-
- CRYPTO IRA
- PRICES & STATS
- RETIREMENT PLANS
- BLOG
 Questions? Call (888) 820 1042
Questions? Call (888) 820 1042
Gold IRA Tax Rules: All You Need to Know
Disclosure: Our content does not constitute financial advice. Speak to your financial advisor. We may earn money from companies reviewed. Learn more
Last Updated on: 4th May 2022, 07:23 am
The current economic scenario doesn’t look too rosy when it comes to inflation and growth. Most analysts are predicting that inflation is here to stay, and it may cause economic growth to stagnate. All the while, the Federal Reserve is set to implement the largest round of interest rate hikes in decades.
The above factors bode for a poor performance from traditional assets such as stock and bonds. Investors are looking for ways to invest money that will protect them from inflation, a weak economy, and perhaps give some growth in value.
Gold is the precious metal of excellence; it has been with us for millennia and is a well-established store of value. You can buy gold on your own at the various bullion dealers available. You would then need to store it, either at home or in a storage facility.
However, gold returns are taxable for the IRS, and you have more tax-efficient options such as an IRA. These retirement accounts allow you to benefit from tax-deferred income while you hold your gold in the IRA. Let's take a look at the ins and outs of holding gold in an IRA and the gold IRA tax rules.
Table of Contents
Can You Hold Physical Gold in an IRA?
You can hold physical gold in an IRA as long as the precious metal meets IRS requirements. You must hold gold and other precious metals in a Self-Directed IRA. The Self-Directed IRA allows investors to hold other assets beyond the traditional stocks and bonds.
You can choose between a Traditional or Roth when you set up your IRA. The Traditional IRA allows you to deduct your contributions from your tax claim. Your investments inside the IRA grow tax-free, and you pay taxes at your going income tax rate when you take distributions.
With a Roth IRA, you make contributions to your plan after tax. Your investments also grow tax-free, but you will not pay taxes when you take distributions. This option is particularly interesting if you believe you will be in a higher income tax bracket at retirement.
IRS Requirements for Precious Metals
The IRS allows investors to hold four types of precious metals as long as they meet the criteria outlined further down.
You can purchase any of the following four precious metals for your IRA:
- Gold
- Silver
- Platinum
- Palladium
All precious metals must meet the purity standards set by the IRS. They must also be minted by a government mint or accredited facility. Gold must have a fineness or purity of 99.5%, the gold can be in bullion or coins.
Some examples of gold coins include the American Buffalo, the Australian Kangaroo, and the Canadian Maple Leaf. American Eagle gold coins are also accepted, even though their purity is slightly lower than 99.5%.
Silver coins and bars must have a purity of 99.9%, while platinum and palladium coins and bars must both have a purity of 9.95%. Precious metals held in an IRA must be considered bullion, that is to say, they do not have any collectible value.
This aspect is something to consider when buying gold coins in particular. Some coins have a numismatic value that can increase the price of your coin way beyond the limits allowed by the IRS. The limit on variation between the spot price of gold and the value of your gold purchases is 10%.
The IRS sets the limits on gold with collectible value to protect investors from buying into assets that may lose a considerable portion of their value if their collectible appeal changes. Your gold IRA company should be able to advise you on which coins you can purchase for your IRA.
Purchasing Gold for Your IRA
To maintain the tax benefits, you cannot add gold you already own to your Self-Directed IRA; you must purchase the gold with funds through the IRA. If you do already own gold, you could sell the gold, then fund your IRA account with the proceeds and buy gold again through the IRA.
You must purchase the gold for your IRA through your custodian. A custodian is an IRS accredited financial institution responsible for the purchase and safety of your assets. Your IRA company will be able to offer this service, either through an existing relationship with an external custodian or as part of their organization.
To fund your IRA to make the purchases in gold you can typically use one of the following ways:
- Complete a rollover: If you have assets in a 401(k) or other types of retirement account, you can roll these assets into your Self-Directed IRA to make precious metal purchases.
- Transfer IRA assets: You may already have investments in an IRA, you can transfer these stocks, bonds, or cash into your gold IRA. You can then use them to buy gold or other precious metals.
- Depositing cash: You can make a wire transfer from your bank account, once the cash is available in your IRA, you can use it to purchase gold.
Not all custodians offer the same quality of service or costs. Ask yourself the following questions when considering who to choose to look after your assets:
- What are their fees for storage and account maintenance?
- How many years has the custodian operated its business?
- Does the company have excellent customer reviews?
- Does the company have good ratings with the Better Business Bureau or similar organizations?
- Is the Custodian approved by the IRS?
Gold IRA Storage
Among gold IRA tax rules, you are obligated to store your gold holdings with an IRS-approved depository. If you take possession of your gold from your IRA, even just for one day, you may find the IRS considers you to have taken a distribution. Early distributions may be subject to penalties and taxes.
Your custodian will have arrangements with a depository, or you may be able to search for your own. In either case, the depository must be approved by the IRS for you to maintain your tax benefits. A few things to consider when choosing a depository:
- How secure is the facility?
- What are the policies of the depository’s insurance?
- What are the storage fees?
The depository takes the responsibility of storing your gold for you until you either sell the precious metal or take a distribution. When the time comes, the depository will send your gold to your home address by secure delivery.
Contribution Limits
The IRS limits the yearly contributions you can make to your IRA but will usually increase them from time to time. Contribution limits for 2021 and 2022 are $6,000, or $7,000 if you are over the age of 50. This is the amount you can contribute to an IRA and benefit from the plan’s special tax status.
There is also another limitation if you already have a retirement plan through your employer and make more than a specified income. The IRS reduces your contribution limit for an IRA on a tax-deferred basis or cancels the tax perk altogether. The table below shows the various income situations and tax filings that determine if you can contribute tax-free dollars to your IRA.
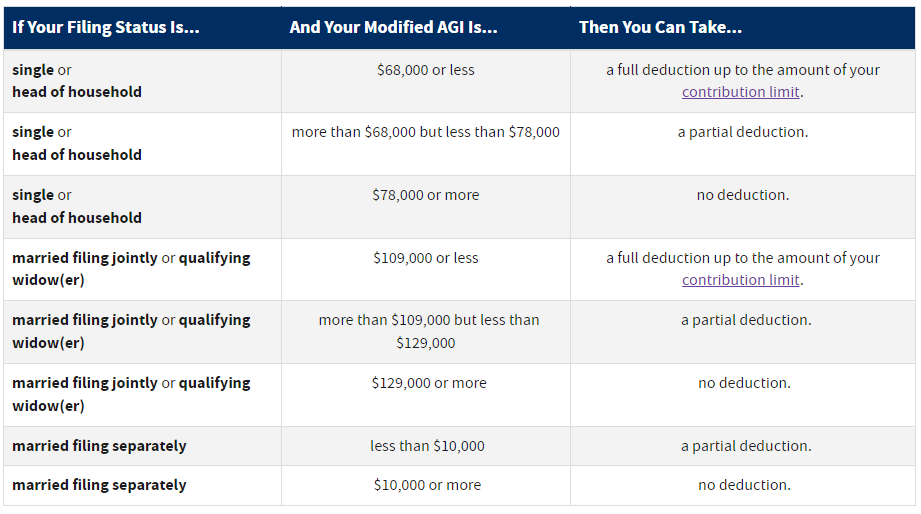
Source: IRS
Modified AGI (Adjusted Gross Income) is your income as it figures on your federal income tax return, before counting for any student loan interest.
If you are married, filing jointly, and your income is equal to or greater than $129,000 your contributions do not qualify for tax deductions. If your income is greater than $109,000 then your contributions qualify for a partial tax deduction. You get a full deduction on your contributions when you make $109,000 or less.
For those who are single, your contributions qualify for a full deduction if you make $68,000 or less. If your income is greater than $68,000 and less than $ 78,000 your contributions qualify for a partial deduction. If your income is greater than $78,000 your contributions have no deduction.
Distribution Limits & Requirements
The tax benefits inherent to an IRA are designed for you to gain the growth of your assets in a tax-free environment. The idea is that you will keep your investments in the account until retirement. Any early distributions or withdrawals, from the retirement plan, may come with a penalty or extra taxes.
If you do make an early distribution from your IRA, you may be subject to a 10% penalty and a capital gains tax if your precious metals have increased in value while in the IRA.
IRS rules for IRAs stipulate that until you turn 59 ½ you cannot take any distributions, although there are some exceptions. You can make an early withdrawal if you suffer a permanent disability, or you want to buy a home for the first time. Further exceptions to avoid paying a 10% penalty include but are not limited to:
- Death of the owner of the IRA
- Transfer to an alternative payee with a qualifying domestic relation
- Qualifying higher education expenses
- Reimbursement of medical expenses, greater than 10% of AGI for 2021
- To pay health insurance premiums while unemployed
Required Minimum Distributions
At the age of 72, you must take required mandatory distributions (RMD) from your IRA, regardless of whether you have retired. The RMDs must begin by the following April 1, after the year in which you reached age 72. However, the RMD rule does not apply if you own a Roth IRA.
The IRS indicates how you must calculate the minimum RMD you should take for each IRA account. The method used is as follows; you take the value of the IRA on December 31, the year before the year you reached age 72. You then divide that sum by the number given in the life expectancy tables from the IRS.
Using a numerical example, let’s say you have $274,000 in your IRA on December 31, the year before you reach 72. The life expectancy from the IRS table III gives you the number 27.4. You then divide $274,000 by 27.4 which equals $10,000. This amount would be the RMD you must take from your IRA.
If you own more than one IRA, you must calculate the RMD for each IRA separately. However, you may withdraw the full sum of those amounts from one or more IRA accounts. You are not obligated to make distributions from each IRA for every RMD you calculated.
You can, of course, withdraw a larger amount than the RMD. However, if you take more than your RMD in any given year it does not add a credit to your RMD for the following year. The RMD will remain the same for this year even if the previous year you took a distribution that was higher than the RMD.
Wrapping Up
Always seek the opinion of a professional tax advisor. IRA accounts are complex and have variations and caveats that you and your advisor must address for each particular situation. What we have seen is a general outline of gold IRA tax rules.
To get yourself started with a gold IRA, you need to find out more about the top companies that offer specialized services for precious metals retirement investing. You can read more about the top-rated gold IRA companies and the services they offer in our review.


 Silver
Silver Gold
Gold Platinum
Platinum Palladium
Palladium Bitcoin
Bitcoin Ethereum
Ethereum
 Gold: $2,387.15
Gold: $2,387.15
 Silver: $27.92
Silver: $27.92
 Platinum: $931.67
Platinum: $931.67
 Palladium: $903.43
Palladium: $903.43
 Bitcoin: $67,909.13
Bitcoin: $67,909.13
 Ethereum: $3,254.68
Ethereum: $3,254.68