ESG Index: What It Is, and Why Alternative Investors Should Care About It
Disclosure: We are reader-supported. If you purchase from a link on our site, we may earn a commission. Learn more
Last Updated on: 5th October 2022, 04:17 pm
Environmental, social and governance (or ESG) is an umbrella term used to describe an organization's interest in prioritizing environmental sustainability and ethical practices in its business operations.
ESGs and ESG indexes are becoming so popular that wealth advisors like Wealthfront and Betterment give their investors the option of investing in ESG indexes as part of their custom portfolios. These indices can be invested in through regular IRA or 401(k) retirement accounts.
Now that ESG companies are gaining traction among investors, you may think there's plenty of opportunity in the space. However, investing in the ESG index isn't right for everyone. This article will discuss ESG companies, the pros and cons of ESG investing, and why alternative investors should care about the ESG index in 2022 and beyond.
Table of Contents
What is ESG?
The first part of ESG is the environmental impact that companies have concerning their business operations. Environmental factors that ESG companies may target include:
- Air quality efforts
- Clean energy
- Waste management
- Deforestation
- Water quality
- Pollution
ESG companies aim to target and reverse the effects of climate change we've seen in the last decade by designing their business model to limit our impact on the environment.
The social component of ESG companies deals with how the organization interacts with its local and national communities. Socially responsible companies are involved in efforts to reduce racism and social stigmas by advocating for:
- Equal human rights
- Fair labor practices
- Diversity in the workplace
These companies may also participate in data protection, privacy, and security efforts for consumers and corporations.
Governance deals with the processes companies use to audit themselves to maintain a high standard of quality throughout the organization. This primarily deals with internal affairs and policing within companies and their policies and regulations. Other types of governance include:
- Diversity
- Executive compensation
- Lobbying
- Whistleblower programs
Using ethical business practices, ESG companies do good for the environment and society while advancing their financial interests. The role of ESG companies is to ensure accountability and systems to manage a corporation's environmental and social impact, especially its carbon footprint.
What is the ESG Index?
The ESG index may refer to a number of different stock indexes composed of ESG companies. One of the largest providers of ESG indexes is MSCI Inc. which has over 1,500 equity and fixed income ESG indexes spanning many different industries and verticals.
Other popular ESG indexes include:
- Nasdaq-100 ESG Index (NDXESG)
- S&P 500 ESG Index (SPXESUP)
- Vanguard FTSE Social Index Fund (VFTAX)
- Parnassus Core Equity Investor (PRBLX)
ESG indexes work the same way as traditional indexes like the S&P 500 or the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA). These indexes are comprised of many different companies across an industry or sector.
ESG indexes, for example, have a collection of companies vetted as ESG organizations that meet specific ESG metrics and standards. If one ESG company in the index loses value, your overall investment will most likely be safe since you're diversified with other ESG companies in your fund.
See below for an idea of how the S&P ESG index compared with the S&P 500: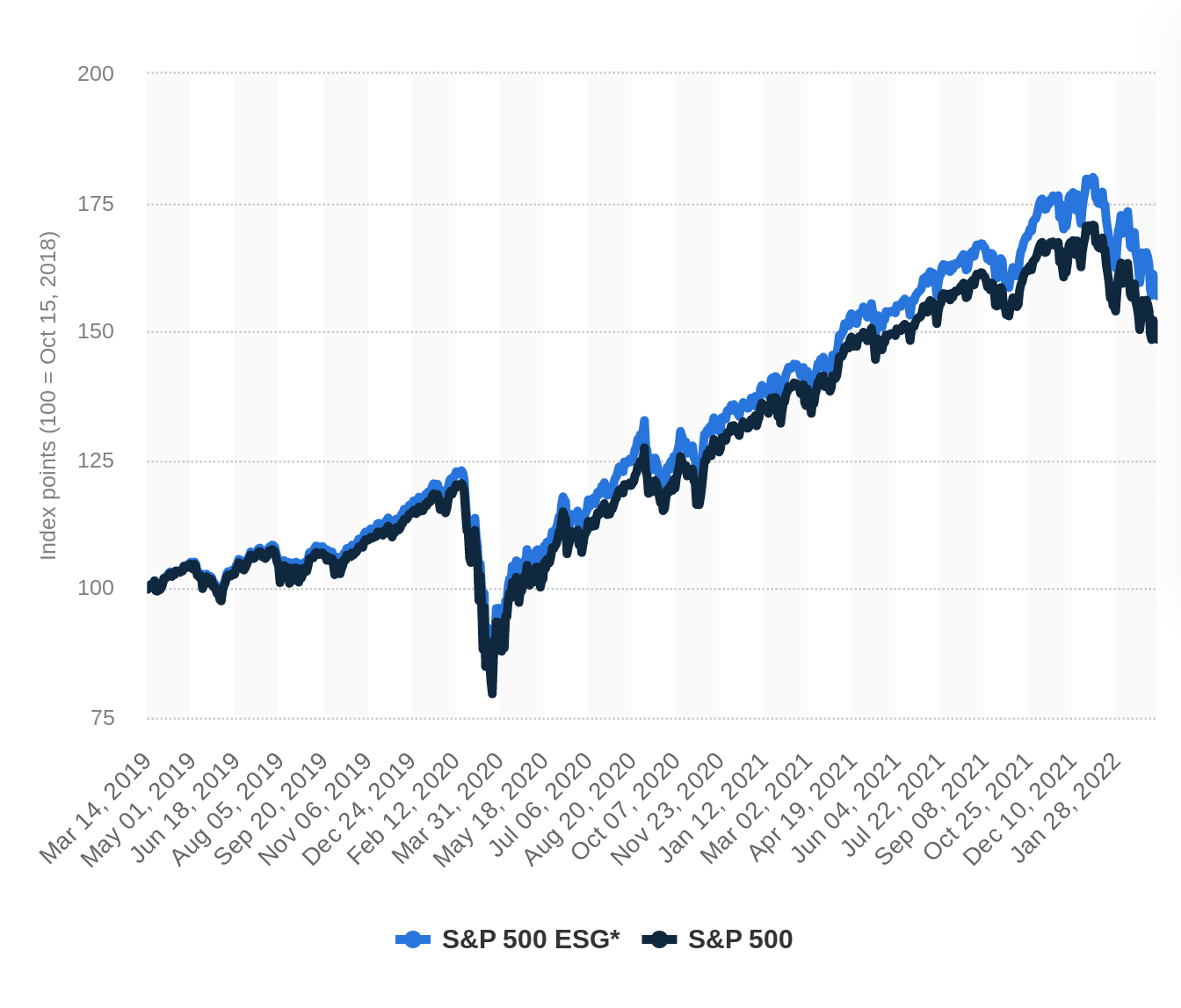
ESG Metrics
Executives and stakeholders use common ESG metrics to gauge the effectiveness of the company's ESG efforts. These metrics also allow the leadership teams to gain insight into the risk factors and areas the business needs to improve upon. Tracking ESG metrics is a great way to attract new investors and acquire customers more efficiently.
ESG metrics can be used in many different ways. However, they primarily aim to measure, report, and improve environmental and social performance and operational efficiency. Using ESG metrics effectively may allow your company to cut costs and improve your bottom line.
Other goals of ESG metrics include:
- Building trust and credibility with stakeholders to attract additional investments
- Encouraging transparency among companies when dealing with environmental and social sustainability efforts
- Helping companies accurately track their progress toward sustainability initiatives and goals
- Reduce expenses by optimizing operations within the company
ESG metrics have several benefits. Companies that regularly track ESG metrics often have a positive image in the eyes of investors when compared to competing companies. If you can convince the public that you're a more sustainable company than competitors, you'll likely benefit from an increase in revenue and word-of-mouth referrals.
While ESG metrics are important for executives, shareholders, and customers, not all companies embrace ESG metrics. Some companies prefer not to use these metrics because the information may lead to internal conflict within the company. Instances may arise where employees think what they're doing is ethical, but customers don't feel the same way. This may lead to disagreements on how to move the company forward.
Additionally, tracking ESG metrics can be costly. New and innovative companies without venture capital backing may not have the working capital to allocate to tracking ESG metrics. Executives may decide that the money needed to track ESG metrics is better used in other areas of the business.
Common ESG Metrics
Since ESG companies span a wide range of industries and verticals, there are no commonly agreed upon metrics that ESG companies must track. However, some common ESG metrics include:
- Water consumption
- Employee safety records
- Greenhouse gas emissions
- Pollution levels
- Waste generation
Alternative investors should consider whether or not ESG companies are keeping up with industry standards of ESG metrics before investing in any ESG company or index. Some market sectors, such as mining, are not known for living up to high environmental standards. However, if you carefully vet the top-ranked uranium stocks you can find companies that respect ESG criteria. The point is, using ESG criteria can allow you to find ethical, future-oriented companies even in fields where environmental standards are considered to be poor.
Pros of ESG Investing
The most obvious benefit for retail investors who invest in ESG companies is that you're doing your part in helping to save the environment, preserve resources, or whatever other mission the ESG companies you invest set forth to accomplish. Since the Industrial Revolution, humans have been depleting the earth of its natural resources at an unsustainable pace. Investing in ESG companies helps to reduce our carbon footprint and impact on the environment.
ESG investing also has social benefits for the community that the companies serve. ESG companies with national or global reach can help serve communities across the world with their mission and have an impact on people outside of their local community.
There is evidence that ESG investing may lead to higher returns compared to traditional investments. One Morgan Stanley white paper published in 2019 found that over the past 18 years, ESG mutual funds kept up with the pace of stock indexes and may have even outperformed them.
Investing in ESG companies and stock indexes may also help with diversification. Data shows that sustainable funds share lower risk factors compared to mainstream stocks. Traditional funds historically have a higher potential for loss, while ESG companies have been relatively stable through many financial cycles.
ESG companies also typically have a lower cost structure and can operate more efficiently than traditional Fortune 500 companies. ESG companies don't spend money on extensive advertising campaigns or expensive perks for their executive team. These companies have fewer expenses and can put their profits right back into the business.
Cons of ESG Investing
While there are plenty of reasons to start investing in ESG companies, there are some downsides that any savvy investor should be aware of before making any investment decisions.
First, you have to spend time researching ESG companies and the missions they support. Investors looking to support specific initiatives need to understand which companies they invest in and how they impact the environment and social landscape.
The SEC also has no clear ESG standards. This means that each company manages its own reporting since oversight is loose on ESG companies. Several initiatives aim to set international standards for ESG companies and how they handle their reporting and metrics shown to the public, but they are still several years away from making an impact.
Types of ESG Investments
There are several different types of ESG investments available today, all carrying different risk profiles. Below are a few of the most common types of ESG investments.
ESG stocks are one of the main ways that people can invest in ESG companies. However, you'll want to ensure that you don't put “all your eggs in one basket” by only holding a few ESG stocks. The best way to diversify your investments is to invest in ESG indexes that sometimes contain hundreds of ESG companies. This ensures you won't lose a substantial amount of your investment if one company fails.
ESG mutual funds are the bread and butter of ESG investing. They are the best way for new investors to support ESG companies and mitigate much of the risk you'd assume if you were investing in individual ESG stocks. ESG mutual funds have become more popular in recent years. In fact, there were 303 ESG mutual funds in 2019, up from 270 in 2018.
ESG Strategy
There are four common approaches to ESG strategy, including:
- ESG integration
- Exclusionary investing
- Inclusionary investing
- Impact investing
ESG integration happens when investors want to integrate ESG factors along with traditional factors to assess the risk and reward of their investment. This ESG strategy may use metrics like water usage or carbon emissions with financial data to identify future risks and opportunities.
Exclusionary investing allows the investor to exclude certain types of ESG companies from their investments. For example, investors may avoid companies that produce tobacco or use fossil fuels in their business operations. With exclusionary investing, investors can effectively eliminate companies that don't meet their criteria for sustainability.
Inclusionary investing is an ESG strategy that allows investors to seek companies that are leaders in their space. Funds may include several leading companies in their sectors and pool them together into a single package.
Impact investing is the last type of ESG strategy that often delivers measurable environmental impact and healthy financial returns. Impact investing focuses on renewable energy companies whose mission is to make the environment cleaner and safer.
Should Alternative Investors Care About the ESG index?
ESG investing is becoming an important part of the economy that not only generates high returns but also helps to save the environment and reduce our carbon footprint. You can help make the world a better place by supporting ESG companies and investing in their indexes.
How to Start Investing in ESG Companies
Traditionally, you'd have to call your broker or advisor and tell them you want to invest in ESG companies. However, today most people are confident enough to handle their investments independently. Services like Robinhood make it very easy for retail investors to manage their money and make smart investment decisions.
First, you'll need to decide whether you'd like to invest in ESG companies on your own or get help from others. Assuming you'd like to start investing on your own, you should research ESG index funds and popular ESG companies that have generated high returns for investors in the past. Then you'll want to open a brokerage account or look into robo-advisors like Betterment or Wealthfront where you can get started choosing ESG indexes.
Alternatively, you can simply set up a self-directed IRA to skip out on the fees and invest directly in whichever assets you choose. Best of all, any capital gains realized within an IRA are exempt from taxation or are tax-deferred, depending on the type of account you choose.
Final Thoughts
ESG companies and indexes are starting to gain traction as we try to mitigate our impact on the environment and reverse the effects of climate change, deforestation, and fossil fuel consumption. Alternative investors may find that ESG indexes are a great way to diversify their portfolio and support the missions of companies leading the way in environmental, social and governance initiatives.
Are you looking to get your investment journey started? To learn more about alternative investments such as gold IRAs, we recommend clicking here and reading about gold IRA rollovers from existing IRAs or 401(k)s. This way, you can reach your financial goals with smart investing, which includes both alternative assets and more traditional stock-based assets, such as ESG indices.


 Silver
Silver Gold
Gold Platinum
Platinum Palladium
Palladium Bitcoin
Bitcoin Ethereum
Ethereum
 Gold: $3,348.95
Gold: $3,348.95
 Silver: $38.17
Silver: $38.17
 Platinum: $1,443.60
Platinum: $1,443.60
 Palladium: $1,294.77
Palladium: $1,294.77
 Bitcoin: $118,036.85
Bitcoin: $118,036.85
 Ethereum: $3,549.24
Ethereum: $3,549.24