Biden Inflation Bill: What Investors Need to Know About the Inflation Reduction Act (2022)
Disclosure: We are reader-supported. If you purchase from a link on our site, we may earn a commission. Learn more
The Inflation Reduction Act, referred to by some as the Biden Inflation Bill, unveiled by Chuck Schumer (D-NY) and Joe Manchin (D-WV) on July 27, 2022 aims to ease some of the economic pressures that have led to record-high U.S. inflation so far this year.
Key provisions in the Biden Inflation Bill deal with the environment and energy as well as implications for the financial sector. Lawmakers claim that the Inflation Reduction Act will reduce the deficit by over $300 billion over the next ten years—a bold claim in our eyes.
The Act also strengthens the tax enforcement efforts of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) with a substantial amount of funding to help with their ability to monitor compliance and enforce tax laws more efficiently than current efforts.
The Biden Inflation Bill also includes provisions related to healthcare that aim to expand vaccination efforts and extend the Affordable Care Act for low-income individuals who get their health insurance from the open marketplace.
This article discusses the key provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act, what it intends to achieve, and what the Act means for investors moving forward in today’s recessionary investing climate.
Table of Contents
Provisions of the Biden Inflation Bill
The intentions of the Biden Inflation Bill are obvious– to reduce the effects Americans (and the world) feel from inflation. Since early 2021, the world has been dealing with chip shortages, fuel and energy problems, and supply chain disruptions that drastically increase the price of everyday products and building materials like lumber. We’ve also seen strong consumer demand that supply has been unable to keep up with.
The Biden Inflation Bill is the first step toward easing the effects of inflation for millions of Americans and people worldwide.
The provisions of the Biden Inflation Bill cover three main areas:
- Finance and taxes
- Healthcare
- Environment and energy
Finance and Taxes
The main provisions dealing with finance and taxes set out to reduce the national deficit and give more power to the IRS to enforce its regulations. Below is the summary of key provisions regarding finance and tax:
- Supporting the IRS with an $80 billion investment for enforcement capabilities, taxpayer services, operations support, and information technology (IT) infrastructure upgrades to catch tax evasion and other similar crimes.
- Establishes an alternative minimum tax (AMT) of 15% for all corporations exceeding profits of $1 billion. The AMT tax takes effect in the 2023 fiscal year and only private equity businesses are exempt.
- Creates a 1% excise tax for stock buybacks of publicly traded companies beginning on January 1, 2023.
With these provisions, the Inflation Reduction Act projects that it will reduce the deficit by $300 billion by 2032 with these relief efforts and reduction of inflationary effects. However, whether this will materialize is a matter of debate. The bill includes $740 billion in spending for various programs that provide stricter regulations for investors and tax implications primarily affecting high-net-worth individuals and large corporations.
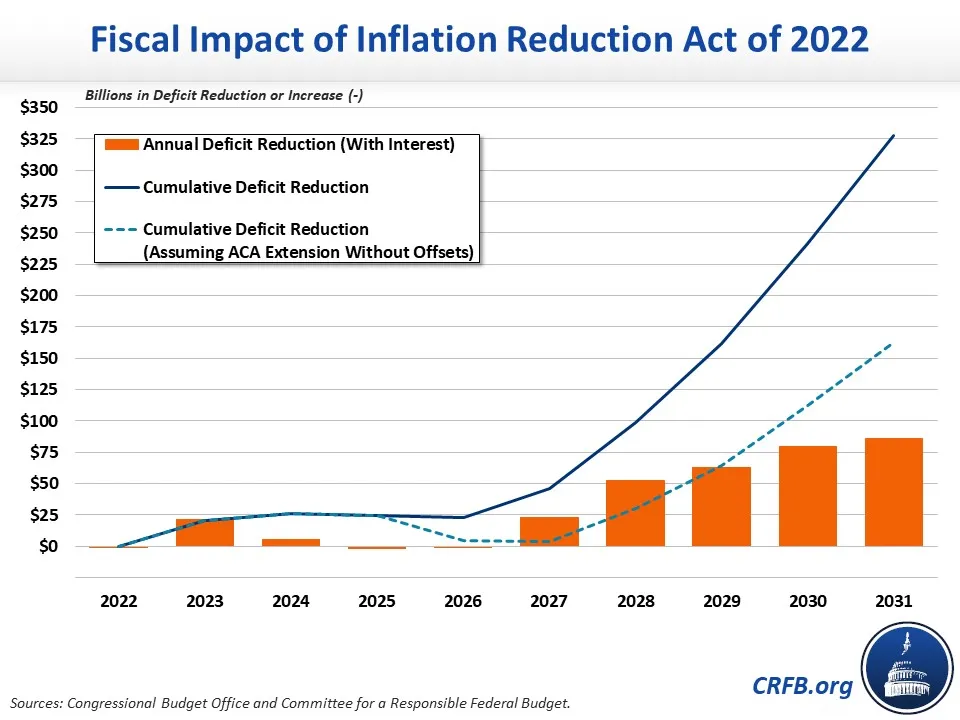
Source: CBO
Healthcare
The healthcare provisions of the bill address out-of-pocket costs for prescriptions and new changes to Medicare policies. See below for a summary of healthcare provisions:
- Affordable Care Act (ACA) receives extended premium subsidies through 2025 in an effort to help low-income earners get qualifying health insurance from the public healthcare marketplace. Current subsidies expire at the end of this year and will be extended another three years with the Inflation Reduction Act.
- The bill reduces the out-of-pocket maximum of prescription drugs for Medicare recipients to $2,000 to limit the number of uninsured patients receiving prescription drugs from county facilities and emergency rooms.
- Expanded coverage for vaccines including COVID, shingles, and other essential vaccines like HPV and measles.
Environment and Energy
Provisions regarding the environment and energy sector are the most comprehensive since these are the main drivers of inflation in the United States. Key provisions include:
- Reducing emissions by funding grants for the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and other government agencies. All U.S. counties can apply for funding through these programs, which include a $7 billion grant intended to assist poor communities and disadvantaged households.
- Extending investment tax credits (ITC) and production tax credits (PTC) for construction projects started before January 1, 2025.
- Carbon capture tax credits extend to construction projects that start before January 1, 2033, and lower the threshold required to meet the qualifications for the tax credit.
- Implementing a Neighborhood Access and Equity Grant program to improve safety in poor communities. The $3 billion program is available for counties that meet eligibility requirements under the program.
Impact on Investors
The Biden Inflation Bill impacts investors in several different ways. First, the stock buybacks reduce the number of shares outstanding for public companies, driving earnings per share higher. Stock buybacks also increase the stock price– an added benefit for investors.
However, the 1% tax may be significant enough for companies to issue dividends instead of stock buybacks and investors may see higher taxes on their capital gains.
High net worth individuals need to make their tax planning a priority with the new enforcement efforts of the IRS which aim to increase revenue by catching tax fraud and issuing fines for violations.
The bill also establishes a limit for losses that companies can use for tax deductions to prevent the ultra-wealthy from eliminating their tax obligations through reported losses.
Business Incentives
Business owners receive some significant incentives with the Inflation Reduction Act, including:
- Tax credits for those who improve the energy efficiency in their commercial buildings.
- Electric vehicle (EV) tax credit up to $7,500 for brand new EVs and up to $4,000 on used EVs.
- Additional tax credits for installing rooftop solar panels, energy-efficient heat pumps, and small energy systems to harness wind energy. Business owners receive a 30 percent credit through 2032 after which it reduces.
- Producers of excessive methane gas emissions receive fines.
- Additional $27 billion toward incentive programs for other clean energy technology.
- Support for reducing methane gas emissions in commercial buildings.
Other Provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act
- A $3 billion grant for environmental justice addressing harmful effects of polluting the environment with $20 million for community-level technical assistance through 2026.
- Extension on coal production taxes funding the Black Lung Disability Trust Fund supporting coal miners with the condition.
- Increase in excise tax from 9.7 cents to 16.4 cents for each barrel of petroleum and crude oil in an effort to fund the cleanup efforts of disaster sites.
- Air pollution monitoring grant of $3 billion for disadvantaged communities close to industrial plants.
Tax Consequences
The Inflation Reduction Act doesn’t call for new tax regulations for households making $400,000 or less– which is good news for some families. The bill further expands Premium Tax Credits from the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) by the end of 2025 and establishes a new 15 percent minimum tax on corporate income from companies reporting profits of more than $1 billion.
Macroeconomic Effects
All the Inflation Reduction Act provisions have a major impact on the macroeconomic environment in the United States and worldwide. An analysis from the Wharton School of Business at the University of Pennsylvania found the following macroeconomic effects of the bill:
Interest rates
Unsurprisingly, interest rates fluctuate but trend upward due to the government making additional efforts to slow the effects of inflation on the housing market. During rising interest rate environments, it may be a good idea to invest in IRA-approved precious metals to help offset inflation and interest rate risks.
Higher Personal and Business Taxes
The bill increases personal and business taxes paid to the government, reducing the U.S. deficit by over 8 percent by 2050. The decrease in government debt pulls in substantial amounts of productive private capital but is offset by the consequences of the increase in personal and business taxes.
Increase in GDP
Any increase in the United States' gross domestic product (GDP) is a positive side effect and experts predict that it will increase slightly by 2040 as a result of the provisions of the Inflation Reduction Act.
Reduced Incentive to Work
While the government expands the Affordable Care Act (ACA) coverage to low-income individuals, one consequence is that it lowers the incentive for unemployed workers to find jobs. Lowering incentives for work contributes to the projected decline in hours worked over the next several years.
Higher Government Spending
The extension of the Affordable Care Act permanently increases government spending to continue to fund these programs. However, higher government spending leads to a decline in government debt, projected to fall by about 7 percent by 2050.
Consequences of the Biden Inflation Bill
The Biden Inflation Bill has a ripple effect on countries outside the United States as well. Below are some additional consequences of the bill:
- A sharp rise in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) attributed to price hikes on gasoline, housing, and food products.
- Interest rate hikes. The Federal Reserve increased interest rates for the third time in 2022 due to housing market concerns.
- Inflation still outpaces job growth and consumer spending, while the minimum wage is worth the lowest since 1956.
What the Biden Inflation Bill Means For You
The Inflation Reduction Act is the federal government’s effort to reduce the substantial effects of the runaway inflation we’re currently experiencing. While knowing the provisions of the bill and the macroeconomic effects are helpful, you should also know what this means for you and your family.
We’ve learned that we can’t trust the government be able to control inflation. Even with robust job growth, inflation outpaces most American’s salaries and bonuses. Luckily, there is a solution to diversifying your investment portfolio that you can use for protection and wealth preservation.
Gold and precious metals provide diversification for building safer, more resilient retirement portfolios that better withstand the effects of inflation.
We encourage you to take a look at our complete guide to opening and managing a gold IRA to find out how you can start using gold and precious metals to safeguard your retirement and diversify your portfolio today.


 Silver
Silver Gold
Gold Platinum
Platinum Palladium
Palladium Bitcoin
Bitcoin Ethereum
Ethereum
 Gold: $4,000.81
Gold: $4,000.81
 Silver: $48.33
Silver: $48.33
 Platinum: $1,547.51
Platinum: $1,547.51
 Palladium: $1,394.31
Palladium: $1,394.31
 Bitcoin: $102,394.72
Bitcoin: $102,394.72
 Ethereum: $3,436.37
Ethereum: $3,436.37