401a vs. 401k: Which Should You Choose? + Key Differences Explained
Disclosure: We are reader-supported. If you purchase from a link on our site, we may earn a commission. Learn more
Last Updated on: 27th August 2024, 09:33 pm
Let's compare 401a vs 401k retirement plans. In this article, we'll go through the key differences between these company-sponsored plans. The 401k plan is the primary retirement plan offered by most employers.
These employers are usually private corporations and businesses. While a 401a is usually offered by nonprofit organizations and public employers like town halls, government, and schools. In most cases, not every public or nonprofit employee is eligible for a 401a but it’s important to understand the differences.

Table of Contents
401k: What Is it? How does it work?
The plan allows employees to make contributions to the savings plan that will grow in a tax-enhanced environment. Most 401k plans are set up with pre-tax dollars. However, you can also opt for a Roth 401k where you contribute after-tax dollars.
In either case, your investments while in the 401k plan can grow tax-free. When you retire and take distributions from your plan you won't pay any taxes if you were making Roth contributions. While you will be subject to your current tax bracket at retirement if you made pre-tax contributions.
The 401k retirement plan was set up for employees, but in 2001 congress enacted legislation to introduce 401k plans for self-employed people also. The Solo 401k was introduced under the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of that year.
The plan was established to give self-employed individuals, and spouses, a means to participate in employer-sponsored retirement plans. One of the most attractive features of a 401k plan is that it allows for employers to match the employee’s contribution.
The employer is not under any obligation to do so, however, employer contributions are tax-free and act as an employee benefit to help retain talent. The matched contributions from the employer usually have a vesting period, further motivating employees to remain in the firm.
Distributions have to be taken with a traditional 401k after the age of 70 1/2 and the IRS will consider them as taxable income. However, if you contributed to a Roth 401k then you are exempt from any minimum distribution schedule. As you already paid income tax before investing in the retirement plan.
401a: Main Characteristics
The 401a allows employers to set up retirement savings accounts for select employees. Something that would not be easy to do with a 401k. These plans are often offered in the same way some firms offer stock options. As a way to retain and motivate new employees.
If the employer sponsors a 401a plan the employee is usually required to make yearly contributions. The employer contributes pre-tax dollars, while the employee has a Roth option where they can contribute after-tax dollars. The 401a is usually offered to specific employees with high profiles to attract them to the job and to keep them motivated to remain.
401a plans usually carry vesting periods for the contributions made by the employer. Most vesting schedules require that a percentage of employer contributions are vested every year. However, some vesting schedules only allow for the full sum of employer contributions to become vested after a specified time in the future.
Comparing 401a vs 401k plans
The main difference that immediately stands out when comparing 401a vs 401k plans is the maximum contribution limits. The limits are much higher for 401a plans compared to 401k plans. Having said that, contributions are compulsory for the employee on a 401a plan.
When it comes to the choice of funds available, 401a plans may be limited to less risky investments than 401k plans. However, in both cases, you would not be able to invest in precious metals, real estate, or other alternative assets.
Employers sponsoring 401a plans can pick and choose which employees they wish to sponsor. While 401k plans are sponsored for all employees. Employers of 401k plans that offer contribution matching must do so on a percentage basis and match all employees equally.
Employers sponsoring 401a plans can match contributions at a different percentage limit and dollar amount for each of their employees. While 401a plan employees are obligated to make yearly contributions, employees with a 401k plan may pick and choose which years they contribute to the plan.
Both 401a and 401k plans are subject to a 10 percent penalty if you take early distributions before the age of 59 ½. Early distributions will also be taxed at your going income tax rate.
In the event an employee leaves their workplace, both accounts allow for rollovers into other retirement accounts. Employees who change jobs may also have the option of rolling over to an IRA account.
Contribution Limits: 401a vs 401k
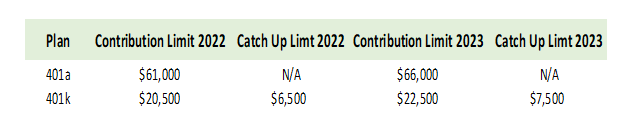
As mentioned above contribution limits for 401a plans are much higher than for 401k plans. Contributions to 401a plans have a limit of $69,000 for 2024. While the contribution limit for 401k plans is $23,000 for 2024.
However, the limit on contributions for 401k is for the employee and the employer can match those amounts. While the contribution limit for a 401a plan is for the combined contribution of employer and employee.
401k plans have a catch-up provision for employees aged 50 ½ and over, meaning you can contribute an extra amount each year. The catch-up limit for 2024 is $8,000. No catch-up limit is available under 401a plans.
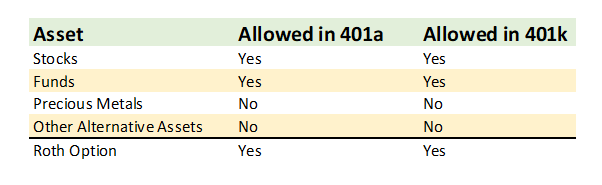
Assets Allowed in a 401a vs 401k
401a and 401k retirement plans have the primary objective of capital protection, and you may generally only invest in stocks, bonds, and funds that invest in these securities. The custodian of the 401a or 401k will determine which funds are available through their services.
Expect to find limitations on which funds you may be able to invest in when contributing to a 401a.
Bottom Line
Saving for retirement can be a tricky business, we need the right knowledge and awareness to navigate all the rules to comply with the IRS. If you are saving extra with an IRA, you may want to take advantage of self-directed IRAs that offer more freedom as to which assets you can invest in.
However, if you are going to invest in precious metals through an IRA you should really turn to the specialized services of a gold IRA company. They have all the knowledge and expertise regarding which bullion is allowed in an IRA, storage services, and transportation.
We have compiled a list of the top-performing gold IRA companies, you can read our reviews about them here.


 Silver
Silver Gold
Gold Platinum
Platinum Palladium
Palladium Bitcoin
Bitcoin Ethereum
Ethereum
 Gold: $5,061.19
Gold: $5,061.19
 Silver: $82.98
Silver: $82.98
 Platinum: $2,111.30
Platinum: $2,111.30
 Palladium: $1,709.09
Palladium: $1,709.09
 Bitcoin: $66,889.48
Bitcoin: $66,889.48
 Ethereum: $1,939.43
Ethereum: $1,939.43